PPT Ground State Electron Configurations and Term Symbols PowerPoint Presentation ID2043186

The ground state in quantum mechanics is the minimal energy of an atom or molecule. An excited state is any state of energy higher than the ground state which is usually attained by the absorption of energy. Different atoms and molecules are variably excitable meaning that some get excited easily, while others require more energy to be excited.
What Is Ground State in Chemistry?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/94256241-56a1304c5f9b58b7d0bce536.jpg)
Other articles where ground state is discussed: spectroscopy: Basic properties of atoms:.possible energy state (called the ground state) can be excited to a higher state only if energy is added by an amount that is equal to the difference between the two levels. Thus, by measuring the energy of the radiation that has been absorbed by the atom, the difference in…
Ground State Electron Configuration of an Atom Rules, Terms & Examples Video & Lesson

The K energy level can contain a maximum of two electrons. The L energy level can hold up to eight, M up to 18, and N up to 32. The atom in the question, which is in the ground state, contains two electrons. The first electron will occupy the lowest energy level, level K. The second electron will also be found in the K energy level, as this.
Ground State Electron Configuration of V Periodic Table Element

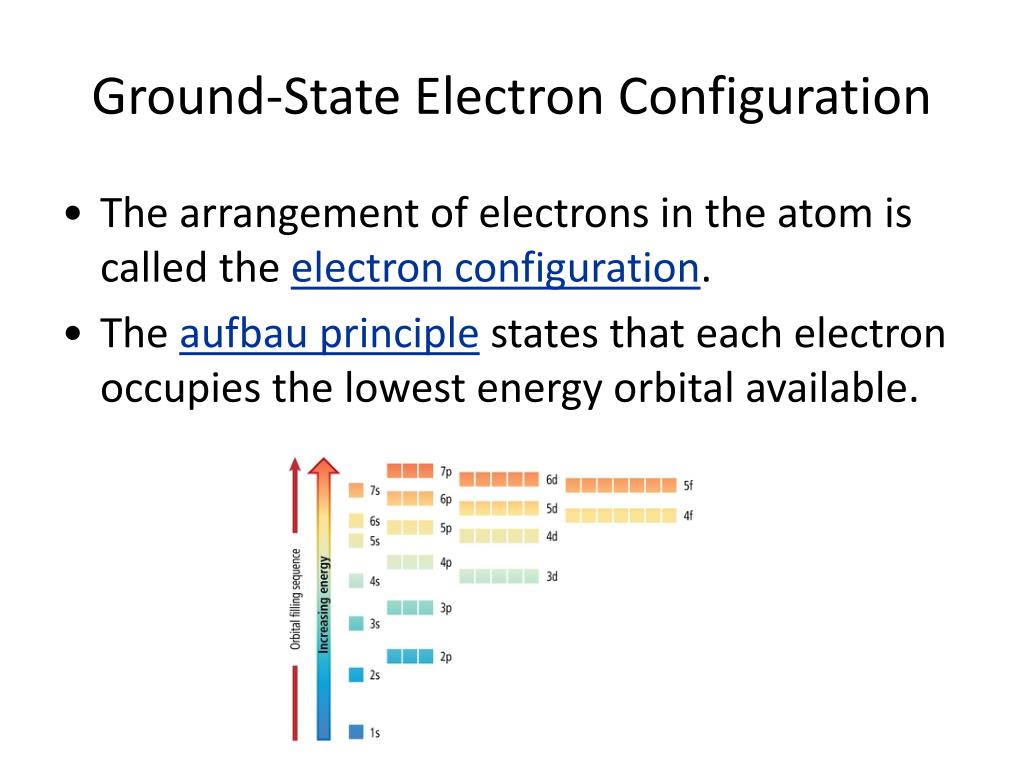
An atom's ground state electron configuration describes how the electrons have distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. According to the electron configuration chart , electrons in an atom occupy orbitals according to their increasing energy, with each orbital having a maximum of two paired electrons with opposite spins .
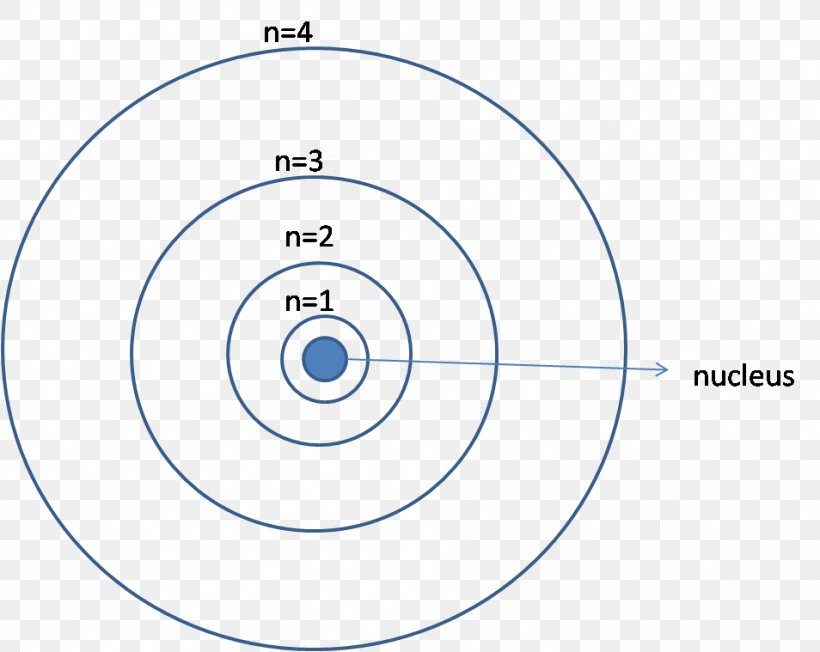
Bohr's atomic model tecscience
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ).
What is ground state electron configuration examquiz
1.9A: Ground State Electronic Configurations. Ground state electron configurations are the foundation for understanding molecular bonding, properties, and structures. From the electrons in an atom, to the differing orbitals and hybridization, the ground state electron configuration sheds light on many different atomic properties.
Ground State Atom Chemistry Libretexts Images
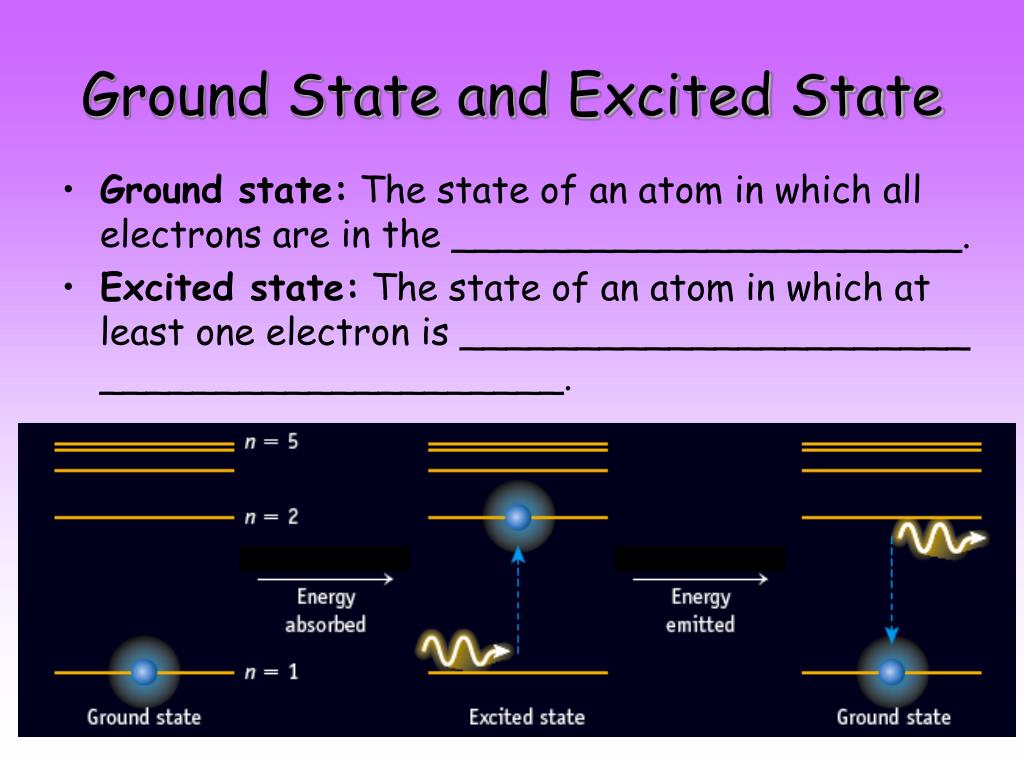
When the electron is in this lowest energy orbit, the atom is said to be in its ground electronic state (or simply ground state). If the atom receives energy from an outside source, it is possible for the electron to move to an orbit with a higher n value and the atom is now in an excited electronic state (or simply an excited state) with a.
Electron Configurations Chemistry Steps
Hydrogen, for instance, has only one electron, which must occupy the lowest-energy orbital. Thus, hydrogen has a 1s ground-state configuration. Carbon has six electrons and the ground-state configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 1 2p y 1, and so forth. Note that a superscript is used to represent the number of electrons in a particular orbital.
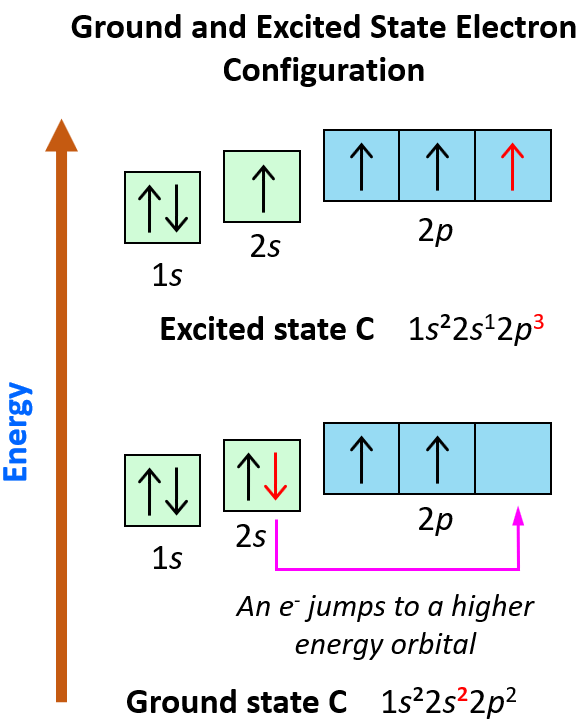
Lewis dot structure of ground state and excited state of carbon YouTube
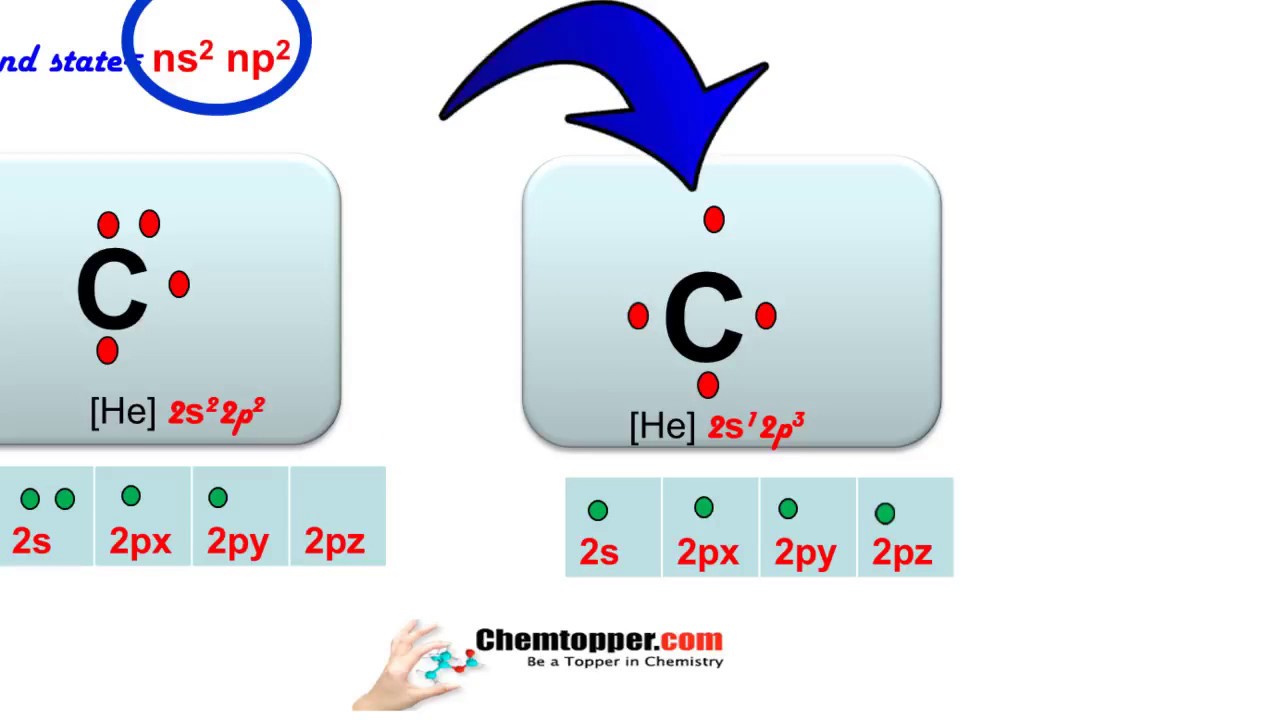
A ground-state atom is an atom in which the total energy of the electrons can not be lowered by transferring one or more electrons to different orbitals. That is, in a ground-state atom, all electrons are in the lowest possible energy levels. eg: Consider a carbon atom whose electron configuration is the following..
Ground State, Excited State, or Impossible Electron Configurations YouTube

The Aufbau Principle (also called the building-up principle or the Aufbau rule) states that, in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill atomic orbitals of the lowest available energy level before occupying higher-energy levels Figure 1.6.1 1.6. 1. In general, an electron will occupy an atomic orbital with the lowest value of n, l,ml.
PPT CHAPTER 5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5502851
The wave function of the ground state of a hydrogen atom is a spherically symmetric distribution centred on the nucleus, which is largest at the center and reduces exponentially at larger distances. The electron is most likely to be found at a distance from the nucleus equal to the Bohr radius. This function is known as the 1s atomic orbital.
Groundstate electron configurations
.PNG)
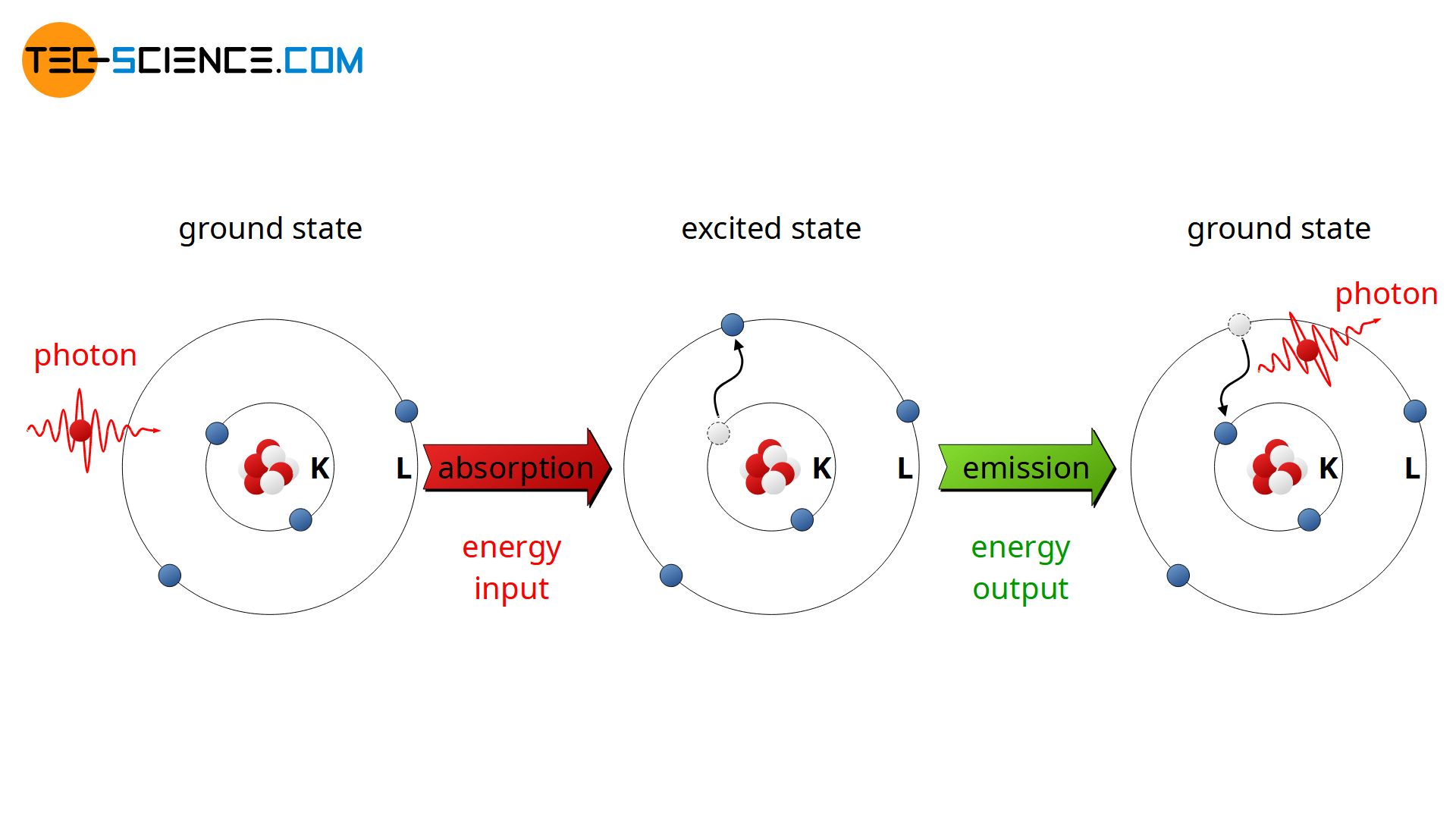
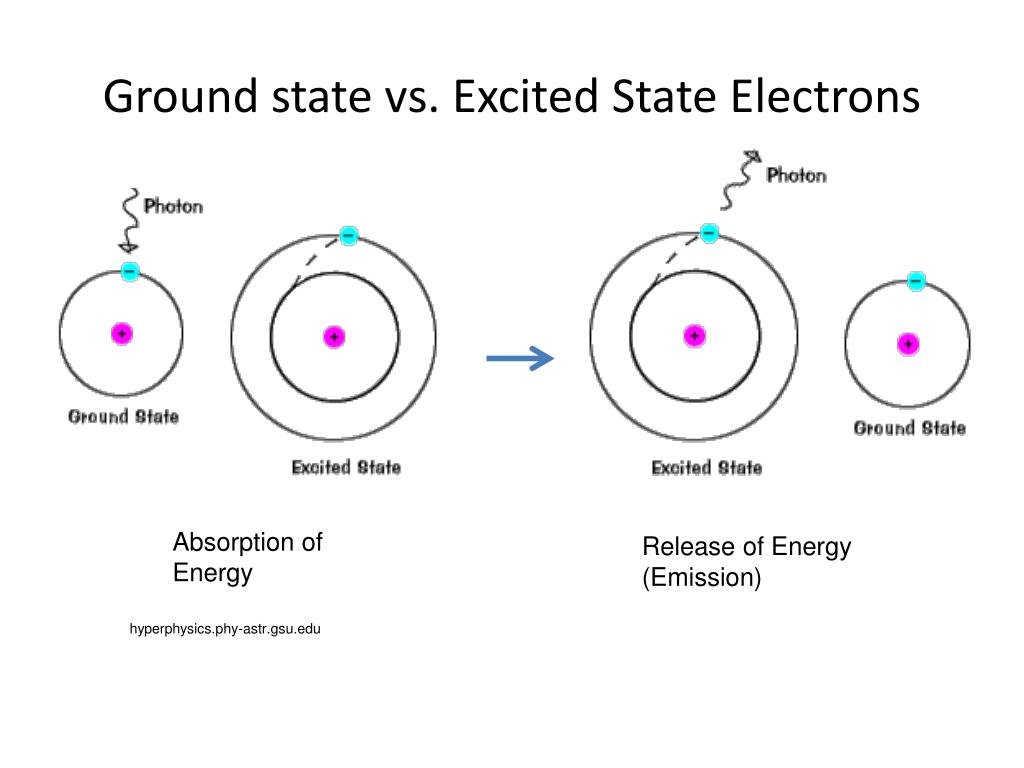
The ground state describes the lowest possible energy that an atom can have. Atoms may occupy different energy states. The energy states are discrete, i.e. they occur at specific values only. Therefore an atom can only move to a new energy level if it absorbs or emits an amount of energy that exactly corresponds to the difference between two energy levels. The lowest possible energy level that.
Ground State Electron Configuration / Ground State Electron Configuration Definition & Example

1. Locate the atom on the periodic table. 2. Locate the noble gas element in the period above the element of interest. 3. Continue the electron configuration from the noble gas until you reach the element of interest. 4. Put the noble gas in brackets and write the remainder of the electron configuration.
PPT Atomic Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID512284
This smallest value of the electron energy in the hydrogen atom is called the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom and its value is \[E_1 = −E_0 = −13.6 \, eV. \label{6.46} \] The hydrogen atom may have other energies that are higher than the ground state. These higher energy states are known as excited energy states of a hydrogen atom.
PPT Unit 6 Electrons in Atoms part 1 properties of waves PowerPoint Presentation ID6499198
The '3s' orbit consists of two and the '3d' orbit consists of zero electrons when the atom is in its ground state. Excited State Electron Configuration : 1s22s22p63s13p33d1. One electron from '3s' orbit moves to the '3d' orbit in its excited state. Both ground and excited states are temporary states.
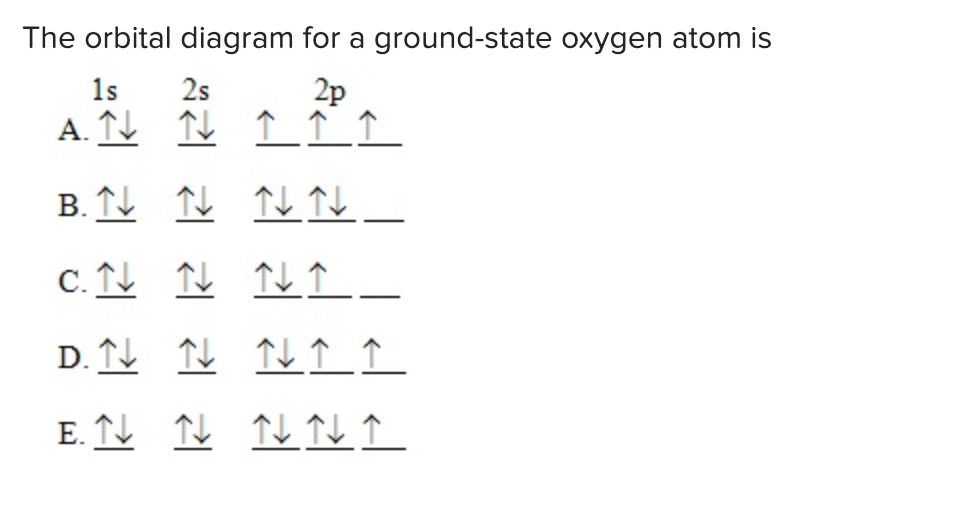
Solved The orbital diagram for a groundstate oxygen atom is
We call the first energy level after the ground state the first excited state. Once the electron's at the higher energy level, it won't stay there long. Electrons, if given the chance, will fall towards the lowest energy level they can. So our electron will fall back down to the ground state and give up four eV of energy.
.